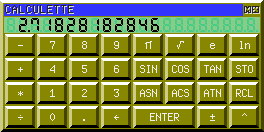Technical pages
Calculations in floating decimal point
Instructions
Use
Example
Principle
Calculations in floating decimal poin
are necessary for the evaluation of mathematical functions and
it is so indispensable to have it in any information system which
respects itself.
I chose normalized size IEEE declined
in simple precision in the mini system and in double precision
in its older brother:
- IEEE simple precision (+/-5,8774e-39
to +/-170,14e36)
- The number is coded on 32 bits:
- - bit 31 for the sign S (0 for a
positive number),
- - bits 30 to 23 for exponent E (8
bits) with a way of 127,
- - bits 22 to 0 for the mantissa
M (23 bits) knowing that bit 23 always in 1 is abolished.
- If E=255 and M#0 then it is no
a number with floating decimal point.
- If E=255 and M=0 then it is infinity
with the sign of S.
- If 0<E<255 then the number
is normalized.
- If E=0 and M#0 then the number is
not normalized .
- If E=0 and M=0 then the number is
0.
- IEEE double precision (+/-11,125e-309
to +/-89,884e306)
- The number is coded on 64 bits:
- - bit 63 for the sign S (0 for a
positive number),
- - bits 62 to 52 for exponent E (11
bits) with a way of 1023,
- - bits 51 to 0 for the mantissa
M (52 bits) knowing that bit 52 always in 1 is abolished.
- If E=2047 and M#0 then it is no
a number with floating decimal point.
- If E=2047 and M=0 then it is infinity
with the sign of S.
- If 0<E<2047 then the number
is normalized.
- If E=0 and M#0 then the number is
not normalized .
- If E=0 and M=0 then the number is
0.
The algorithms of mathematical functions
are based on those presented in the following book:
- "implantation des fonctions
usuelles en 68000"
by François BRET in publishing MASSON.
Certain instructions are limited developments
only used for the elaboration of mathematical functions.

Instructions
WARNING:
"Float" in the list of parameters indicates a 32 bits
number so 1 only stack level for the mini system, and the number
of 64 bits so 2 stack levels for his older brother.
float FNEGATE -float
Opposite value (inversion of S)
float FABS abs(float)
Absolute value (reset of S)
exponent,n* NORM float
Normalization of the mantissa of a number
*: n occupy 2 stack levels in IEEE double
precision
float1,float2 F+ float1+float2
Addition
float1,float2 F- float1-float2
Subtraction
float1,float2 F* float1*float2
Multiplication
float1,float2 F/ float1/float2
Division
float INT n
Float conversion towards signed integer (32
bits)
n UFLOAT float
Conversion signed integer ( 32 bits) towards
float
float,n PUISSANCE float^n
Rise of the float in the power n
float1,float2 F/MOD float1-(n*float2),n
Calculation rest and quotient (signed 32
bits integer) of 2 floats division
float,address FCONVERT float',address'
Conversion of the character string pointed
by address counts it float until the first not convertible character
float <##F#> address,n
Conversion of a float in a string of n characters
pointed by address
6 significant digits in
simple precision and 12 in double precision
float F. -
Displaying of a float on the terminal output
float FSQRT float'
Square root of a float
float FEXP0 float'
Calculation of the exponential of a floa
by limited development
float FLN0 float'
Calculation of the neperian logarithm of
a float by limited development
float FEXP float'
Calculation of the exponential of a float
float FLN float'
Calculation of the neperian logarithm of
a float
- FPI float
Constant PI
float FATAN0 float'
Calculation of the arc - tangente of a floa
by limited development
arc,y,x,ki,fatan(ki) AJUSTEXY
arc',y',x'
Sub-routine for calculation of the tangente
of the angle half
float FTANU float'
Calculation of the tangente of the angle
half
float FTAN float'
Calculation of the tangente
float FSIN float'
Calculation of the sine
float FCOS float'
Calculation of the cosine
float FATAN float'
0Calculation of the arc - tangente
float FASIN float'
Calculation of the arc - sine
float FACOS float'
Calculation of the arc - cosine

Use
As regards the mini system, the instructions
of calculation in floating decimal point are used as those of
integers.
For the main system, it is necessary
to not forget that every floating number decomposes into 2 numbers
on the stack. It is necessary so to take certain precautions to
manipulate them.
Instruction " DUP " should
be replaced afterward " OVER OVER ".
Instruction " DROP " should
be replaced afterward " DROP DROP ".
One can imagine the creation of the
following instructions:
: FDUP OVER OVER ;
: FDROP DROP DROP ;
To you to imagine the equivalent of
the other stack manipulation instructions for the floating numbers
64 bits...

Example
To illustrate this presentation, here
is the result of the calculation of 3 values often used in mathematical
(IEEE double precision):
the constant PI:
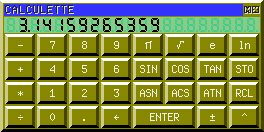
the square root of 2:
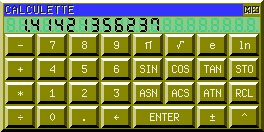
the constant e: